Blow Moulding Bitesize Inc,Asus Router Default Login Rt Ac68p,Delta Radial Arm Saw Parts 20,Aqua Coat Wood Grain Filler 70 - Try Out

Laser cutting does have a high tolerance, especially when […]. Blow moulding products all have one thing in common: they are hollow and in one piece. The process is limited to only making hollow […]. But for some of us, something as simple as taking a breathe is not so straightforward. The team at AirPhysio knew they could help. Like all good ideas, the concept […].
What is Pultrusion? Pultrusion is a process that flips the logic of extrusion. Instead of feeding material into a hopper, and forcing it through a die, the raw material is rolls of pre-impregnated pre-preg fibre filled polymers threads. These threads are pulled through the entire assembly line during setup. The threads from their spools, run […]. Resin Transfer Moulding RTM is a process that injects a two-part resin mixture that fills a mould under high pressure. In the mould there is also a fibre based preform.
As the mould heats, the resin is cured into a solid shape and the part is ejected, with the fibre center preform being wrapped in […]. What is Compression Moulding? The basic principle of Compression Moulding is that you have a pliable or dough-like material, sometimes in a preform or just in granules in two mould halves.
You then […]. Well it uses a super-hot beam of light to melt, burn or vaporises stock material. In certain machines, laser cutting can produce anything from structural welds, clean cuts and even up to very fine […]. Polyamides also known as PA, though commonly referred to as Nylon are a family of engineering grade plastics, which are known for their immense tensile strength and high durability.
They generally are semi-crystalline and have good thermal and chemical resistance. There are various grades of nylons, some common grades are Nylon 6 PA6 , Nylon 6,6, […]. Polypropylene PP is commonly sighted as the second most commonly used plastic on earth, by weight used yearly by industry. Polypropylene was first polymerized in by a pair of Phillips petroleum scientists named Paul Hogan and Robert Banks.
The ability of polypropylene to crystallize created a lot of excitement, and Italian chemist, […]. Previously we discussed Thermoforming, today I wanted to talk about a subsection of that category of plastics manufacturing known as Vacuum Moulding or Vacuum Forming. Thermoforming is one of the most accessible and easy to understand manufacturing processes. For instance, high end boxed chocolates are often arrayed out in their box in a thermoformed tray.
Yoghurt tubs, takeaway food containers, those plastic tubs your cherry […]. Polyurethanes also known as PUR or UR are a massive family of highly versatile engineering materials designed to provide properties not available in conventional rubbers, metals and plastics. Typically they have higher oil and solvent resistance, along with greater abrasion and tear resistance. Impact strength, low compression set and superior load bearing capacity are also […].
ABS is purpose built to be easy, cheap, stiff and tough, all while being capable of displaying great surface finishes and colours. Acrylonitrile is highly process able and glossy. Polyoxymethylene POM , usually referred to as Acetal, is a widely used engineering plastic. Its primary claim to fame is its use in mechanical parts. If it has to bear a load, like a gear, a handle, a zipper or the foot on a piece of furniture, then Acetal is it the material of choice.
As […]. Plastic Co-extrusion is very similar to Plastic Extrusion, however, with co-extrusion you are inserting multiple polymers into the extrusion dies to produce a single profile with a range of physical characteristics. So the fundamental difference to […]. In this article, we will unpack the basic process, advantages and disadvantages of this manufacturing technique and decipher some of the jargon thrown about in the rapid prototyping industry.
Polystyrene PS plastic is a naturally transparent thermoplastic that is available as both a typical solid plastic as well in the form of a rigid foam material.
PS plastic is commonly used in a variety of consumer product applications and is also particularly useful for commercial packaging. Dow Chemical Company invented a proprietary process to […]. Extrusion is a simple process and is used the world over, from making spaghetti to window frames and door seals. Plastic Extrusion is when a material is being forced through a die think a plate with a profile cut into it and Blow Moulding Bitesize Zoom the plastic takes the form of that profile.
In plastics, extrusion creates long strips […]. Polycarbonate is a naturally transparent amorphous thermoplastic. Although made commercially available in a variety of colors, the raw material allows for the internal transmission of light nearly in the same capacity as glass. Blown Film is a manufacturing process that produce films of plastic sheeting and tubes. These sheets or tubes can either be fully cylindrical, or have other object inserted into them so they form useful objects like shopping bags, rubbish bags or cling wrap.
In this article, we will explore what the process of blown film […]. In fact, you probably enjoyed a roto-moulded product over Easter.
Polyvinyl Chloride PVC is an unsung hero of the plastics industry. Whenever there is a dirty outdoor job, PVC is often the go-to material. PVC has been around longer than most plastics having been first synthesized in and commercially produced by B.
Goodrich Company in the s. By comparison, many other common plastics were […]. Much wonderment and applause ensued within the walls…but outside, scepticism was rampant. Many balked. Many were wrong. By the same time the next year, it felt like the whole world either owned an iPhone 1st Gen or intended to. A […]. Polyethylene is the plastic worlds jack of all trades, the ultimate do anything tool. Like all good tools, its power lies in its simplicity.
All […]. Die Casting is the injection of molten metal into a Die similar to a Mould under pressure to create complex parts out of metal. Die Casting is conceptually very similar to injection moulding — just with molten metal instead of plastic.
Die Casting is primarily a mass production method, where the costs of setting up […]. Your concept has left the drawing board and entered the computer realm. As standardized mass production techniques develop to cater for low-grade affordable consumer goods, experts are looking to high-end manufacturers for small batch high-value products. Electronics manufacturers are the first to recognize that quality production techniques are important. Leading manufacturers of audio equipment, testing instruments and automobile parts are pushing the boundaries of quality, diversity and […].
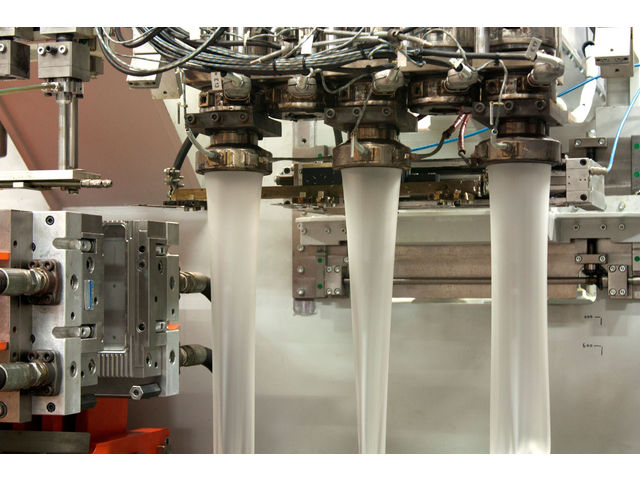
Manufacturing processes hinge on the practice of making large quantities of uniform items. Creating uniform items allows for a standardised quality of product, which is one of the fundamental premises of market economics. The blow molding process begins with melting down the plastic and forming it into a parison or, in the case of injection and injection stretch blow molding ISB , a preform.
The parison is a tube-like piece of plastic with a hole in one end through which compressed air can pass. The parison is then clamped into a mold and air is blown into it. The air pressure then pushes the plastic out to match the mold. Once the plastic has cooled and hardened the mold opens up and the part is ejected.
Water channels are carved into the mold to assist in cooling. The process principle comes from the idea of glassblowing. This was the beginning of the commercial blow molding process. During the s the variety and number of products was still very limited and therefore blow molding did not take off until later.
Once the variety and production rates went up the number of products created soon followed. The technical mechanisms needed to produce hollow bodied workpieces using the blowing technique were established very early on. Because glass is very breakable, after the introduction of plastic, plastic was being used to replace glass in some cases.
The first mass production of plastic bottles was done in America in Germany started using this technology a little bit later, but is currently one of the leading manufacturers of blow molding machines. In the United States soft drink industry , the number of plastic containers went from zero in to ten billion pieces in Today, an even greater number of products are blown and it is expected to keep increasing.
For amorphous metals , also known as bulk metallic glasses, blow molding has been recently demonstrated under pressures and temperatures comparable to plastic blow molding. In extrusion blow molding EBM , plastic is melted and extruded into a hollow tube a parison. This parison is then captured by closing it into a cooled metal mold.
Air is then blown into the parison, inflating it into the shape of the hollow bottle , container, or part. After the plastic has cooled sufficiently, the mold is opened and the part is ejected. Examples parts made by the EBM process: most polyethylene hollow products, milk bottles, shampoo bottles, automotive ducting, watering cans, and hollow industrial parts such as drums.
Straight EBM is a way of propelling material forward similar to injection molding whereby an Archimedean screw turns, then stops and pushes the melt out. With the accumulator method, an accumulator gathers melted plastic and when the previous mold has cooled and enough plastic has accumulated, a rod pushes the melted plastic and forms the parison.
In this case the screw may turn continuously or intermittently. The accumulator head or reciprocating screw methods use hydraulic systems to push the parison out quickly reducing the effect of the weight and allowing precise control over the wall thickness by adjusting the die gap with a parison programming device.
It is also a way of turning into a Accumulator. In continuous extrusion blow molding, the parison is extruded continuously and the individual parts are cut off by a suitable knife.
Containers such as jars often have an excess of material due to the molding process. This is trimmed off by spinning a knife around the container which cuts the material away. This excess plastic is then recycled to create new moldings. The sheet, or "film" when referring to thinner gauges and certain material types, is heated in an oven to a high-enough temperature that permits it to be stretched into or onto a mold and cooled to a finished shape.
Its simplified version is vacuum forming. In its simplest form, a small tabletop or lab size machine can be used to heat small cut sections of plastic sheet and stretch it over a mold using vacuum. This method is often used for sample and prototype parts. In complex and high-volume applications, very large production machines are utilized to heat and form the plastic sheet and trim the formed parts from the sheet in a continuous high-speed process and can produce many thousands of finished parts per hour depending on the machine and mold size and the size of the parts being formed.
Thermoforming differs from injection molding , blow molding , rotational molding and other forms of processing plastics. Thin-gauge thermoforming is primarily the manufacture of disposable cups , containers, lids, trays, blisters , clamshells, and other products for the food , medical , and general retail industries.
Thick-gauge thermoforming includes parts as diverse as vehicle door and dash panels, refrigerator liners, utility vehicle beds and plastic pallets. In the most common method of high-volume, continuous thermoforming of thin-gauge products, plastic sheet is fed from a roll or from an extruder into a set of indexing chains that incorporate pins, or spikes, that pierce the sheet and transport it through an oven for heating to forming temperature.
The heated sheet then indexes into a form station where a mating mold and pressure-box close on the sheet, with vacuum then applied to remove trapped air and to pull the material into or onto the mold along with pressurized air to form the plastic to the detailed shape of the mold. Plug-assists are typically used in addition to vacuum in the case of taller, deeper-draw formed parts in order to provide the needed material distribution and thicknesses in the finished parts.
After a short form cycle, a burst of reverse air pressure is actuated from the vacuum side of the mold as the form tooling opens, commonly referred to as air-eject, to break the vacuum and assist the formed parts off of, or out of, the mold.
A stripper plate may also be utilized on the mold as it opens for ejection of more detailed parts or those with negative-draft, undercut areas. The sheet containing the formed parts then indexes into a trim station on the same machine, where a die cuts the parts from the remaining sheet web or indexes into a separate trim press where the formed parts are trimmed.
The sheet web remaining after the formed parts are trimmed is typically wound onto a take-up reel or fed into an inline granulator for recycling. Most thermoforming companies recycle their scrap and waste plastic, either by compressing in a baling machine or by feeding into a granulator grinder and producing ground flake, for sale to reprocessing companies or re-use in their own facility.
Frequently, scrap and waste plastic from the thermoforming process is converted back into extruded sheet for forming again. Microprocessor and computer controls on more modern machinery allow for greatly increased process control and repeatability of same-job setups from one production run with the ability to save oven heater and process timing settings between jobs.
The ability to place formed sheets into an inline trim station for more precise trim registration has been improved due to the common use of electric servo motors for chain indexing versus air cylinders, gear racks, and clutches on older machines.
Electric servo motors are also used on some modern and more sophisticated forming machines for actuation of the machine platens where form and trim tooling are mounted, rather than air cylinders which have traditionally been the industry standard, giving more precise control over closing and opening speeds and timing of the tooling.
Quartz and radiant-panel oven heaters generally provide more precise and thorough sheet heating over older cal-rod type heaters, and better allow for zoning of ovens into areas of adjustable heat. A new technology, ToolVu, has been developed to provide real-time feedback on thermoformer machines.


|
Wood Burning Stamp Letters Wood For Turning For Sale Quora |
ROYA1
28.10.2020 at 18:32:33
ayka012
28.10.2020 at 11:38:43